The Market Context
Retail trading has undergone a structural transformation driven by cloud computing, edge networking, and mobile-first financial platforms. What was once an institutional privilege is increasingly accessible to individual market participants. Execution speed now represents not merely a technical metric, but a core determinant of trading outcomes.
As emerging markets expand digital participation, brokerage infrastructure becomes a systemic economic variable. Faster execution compresses information asymmetry and reduces frictional costs. This shift positions platform technology as a primary competitive and risk-management differentiator.
Macro-level capital flows increasingly favor environments where transactional certainty exists. Retail traders, in turn, gravitate toward ecosystems that demonstrate consistent performance under volatile conditions. Execution speed thus intersects directly with market confidence and liquidity formation.
Regulatory Infrastructure
Execution quality begins with regulatory architecture rather than application design. Jurisdictions with defined licensing regimes impose capital adequacy standards and operational transparency. These requirements create a baseline for systemic resilience.
Fund segregation remains a cornerstone of credible brokerage operations. Client balances must be operationally separated from corporate accounts to mitigate counterparty risk. This separation supports uninterrupted execution even during firm-level financial stress.
From a macro perspective, regulatory harmonization across regions enhances cross-border liquidity pools. Brokers aligned with multi-jurisdiction compliance frameworks gain access to deeper counterparties. The result is structurally improved execution consistency.
The Latency Equation
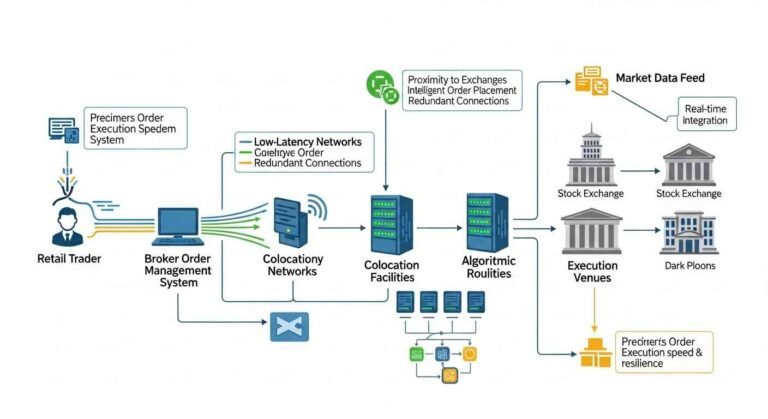
Latency reflects the time between order initiation and final confirmation. Even microsecond differences compound at scale, particularly in fast-moving markets. Brokers engineer infrastructure to minimize physical and logical distance from liquidity sources.
Proximity hosting near exchange servers reduces network hops and packet loss. Simultaneously, optimized order-routing algorithms prioritize venues offering optimal spreads and depth. These technical decisions directly influence slippage and fill ratios.
Execution speed therefore becomes a composite of hardware, networking, and software orchestration. Brokers unable to integrate these layers cohesively face persistent performance degradation. Markets ultimately penalize such inefficiencies through reduced participation.
Liquidity Aggregation Models
Liquidity aggregation consolidates pricing from multiple counterparties into a unified order book. This structure increases available depth at each price level. Greater depth improves execution stability during high-volume periods.
Advanced brokers deploy smart order routers that fragment large orders across venues. This minimizes market impact while preserving execution speed. The outcome is lower slippage without sacrificing timeliness.
In emerging markets, aggregation also mitigates local liquidity fragmentation. By connecting to global pools, brokers enhance execution quality beyond domestic constraints. This connectivity reshapes retail trading viability.
Institutional-grade execution is no longer exclusive to Wall Street; platforms like reliable trading platform demonstrate how modern infrastructure design can translate low-latency aggregation into consistent execution standards for global retail participation.
User Experience (UX) Protocols
Execution speed is partially perceptual, influenced by interface responsiveness. Delayed chart updates or lagging order tickets distort trader decision-making. UX design therefore becomes a functional component of execution management.
Mobile-first architectures prioritize lightweight interfaces and adaptive layouts. These features ensure consistent performance across device classes. Traders increasingly expect parity between desktop and handheld environments.
Integrated charting engines with real-time data feeds reduce cognitive latency. When analysis and execution occur within a single interface, friction declines. This consolidation supports faster reaction cycles.
Risk Management Features
Speed without safeguards magnifies downside exposure. Brokers integrate automated risk controls to prevent catastrophic account depletion. Negative balance protection represents a foundational standard.
Stop-loss and take-profit mechanisms must execute at server level rather than device level. This ensures orders trigger even if user connectivity drops. Reliability under adverse conditions defines operational maturity.
Macro-stability benefits when retail losses are structurally capped. Such safeguards reduce systemic spillover effects. Execution speed must therefore coexist with disciplined risk architecture.
Critical Red Flags
- Absence of disclosed regulatory jurisdiction or licensing identifiers
- Frequent requotes during normal market conditions
- Opaque order-routing descriptions
- Lack of fund segregation disclosures
- Inconsistent platform uptime during high volatility
Data Transparency and Reporting
Advanced brokers publish execution statistics such as average latency and fill rates. These metrics provide empirical insight into platform performance. Transparency functions as a signaling mechanism.
Audit trails further reinforce accountability. Traders can verify timestamped order histories and execution venues. This documentation underpins dispute resolution and trust formation.
From a macro lens, data transparency supports market integrity. It aligns retail infrastructure with institutional disclosure norms. This convergence elevates overall market quality.
Future Outlook
By 2026, artificial intelligence will increasingly orchestrate order routing and liquidity sourcing. Machine learning models will adapt dynamically to market microstructure changes. Execution optimization becomes predictive rather than reactive.
Automation will also extend to compliance monitoring and risk thresholds. Real-time surveillance systems will preemptively flag execution anomalies. This integration enhances systemic resilience.
The trajectory suggests convergence between institutional and retail execution standards. Platform technology becomes the primary differentiator. Brokers capable of sustaining this evolution will shape the next phase of global retail trading.